RHACM GitOps: Install Service Mesh Operator and Configure a default control plan
-
 Jin Zhang
Jin Zhang
- Automation, Aws, Git hub actions
- November 10, 2022
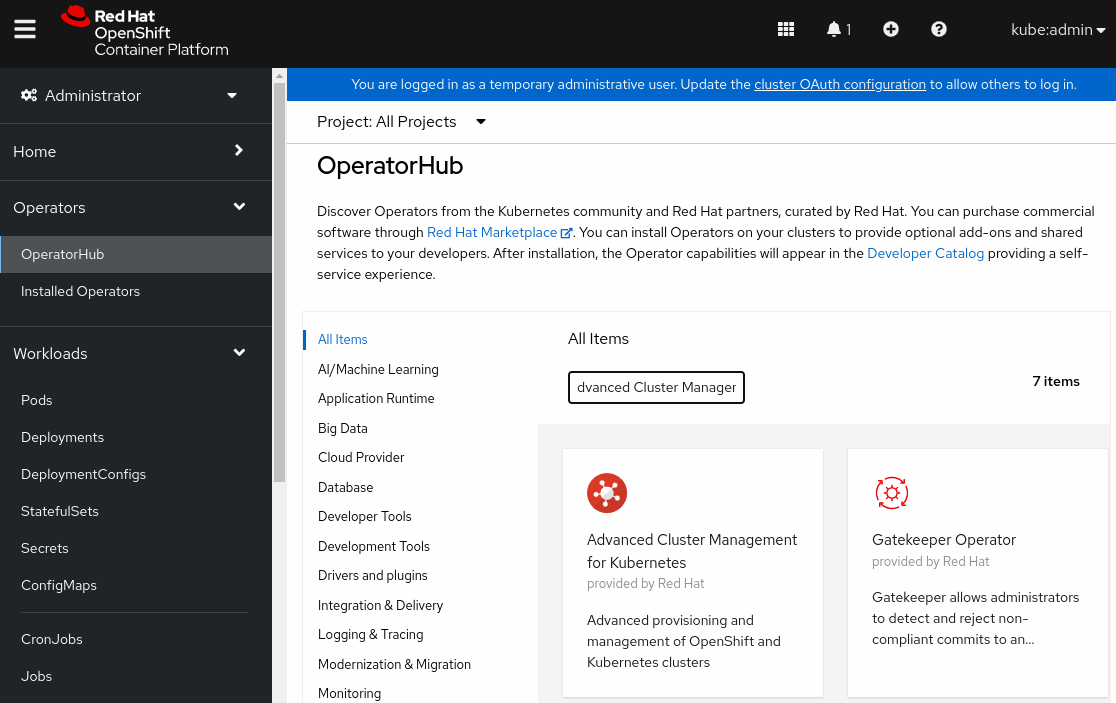
This blog shows how to use RHACM GitOps to install Service Mesh and configure the default control plan.
If your hub and managed clusters are not ready, please refer to https://www.techbeatly.com/install-the-rhacm-operator-import-an-existing-cluster-deploy-a-new-cluster/ for environment setup.
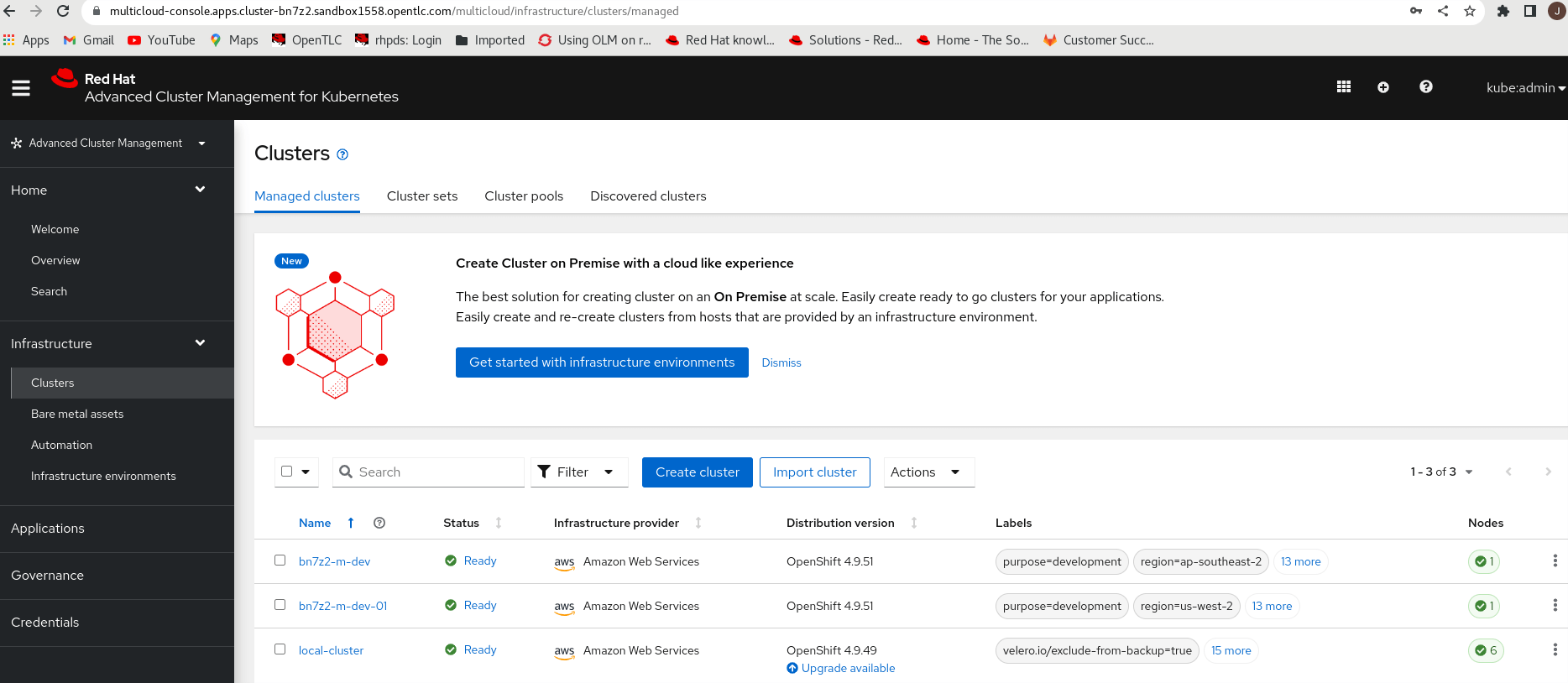
Below are the clusters we use here.
The “local-cluster” is the hub server. The 2 managed clusters are “ bn7z2-m-dev ” and “ bn7z2-m-dev-01 ” with the label “purpose=development”.
GitOps – tempaltes on github
$ git clone https://github.com/alpha-wolf-jin/mesh-apps.git
$ tree ./mesh-apps/
./mesh-apps/
├── elastic-operator
│ └── elasticsearch.yaml
├── jaeger-operator
│ └── jaeger-operator.yaml
├── kiali-servicemesh-operator
│ └── kiali-servicemesh-operator.yaml
├── mesh
│ └── smcp-basic.yaml
└── README.md
Templates used for Service Mesh:
elasticsearch.yaml
Create a Subscription object YAML file to subscribe to elasticsearch-operator in the openshift-operators-redhat namespace.
$ cat elastic-operator/elasticsearch.yaml
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-operator
namespace: openshift-operators-redhat
spec:
channel: stable
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: elasticsearch-operator
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
jaeger.yaml
Create a Subscription object YAML file to subscribe to the jaeger-product in the openshift-distributed-tracing namespace.
$ cat jaeger-operator/jaeger-operator.yaml
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: jaeger-product
namespace: openshift-distributed-tracing
spec:
channel: stable
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: jaeger-product
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
kiali-servicemesh-operator.yaml
Create a Subscription object YAML file to subscribe to the kiali-ossm & servicemeshoperator Operators in the openshift-operators namespace.
$ cat kiali-servicemesh-operator/kiali-servicemesh-operator.yaml
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: kiali-ossm
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
channel: stable
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: kiali-ossm
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: servicemeshoperator
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
channel: stable
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: servicemeshoperator
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
smcp-basic.yaml
Create a ServiceMeshControlPlane object basic in namespace istio-system .
$ cat mesh/smcp-basic.yaml
---
apiVersion: maistra.io/v2
kind: ServiceMeshControlPlane
metadata:
name: basic
namespace: istio-system
spec:
version: v2.2
gateways:
egress:
enabled: true
runtime:
deployment:
autoScaling:
enabled: false
ingress:
enabled: true
runtime:
deployment:
autoScaling:
enabled: false
tracing:
sampling: 10000
type: Jaeger
telemetry:
type: Istiod
policy:
type: Istiod
addons:
grafana:
enabled: true
jaeger:
install:
storage:
type: Memory
kiali:
enabled: true
Managing Multicluster Service Mesh with RHACM GitOps
Application – elastic
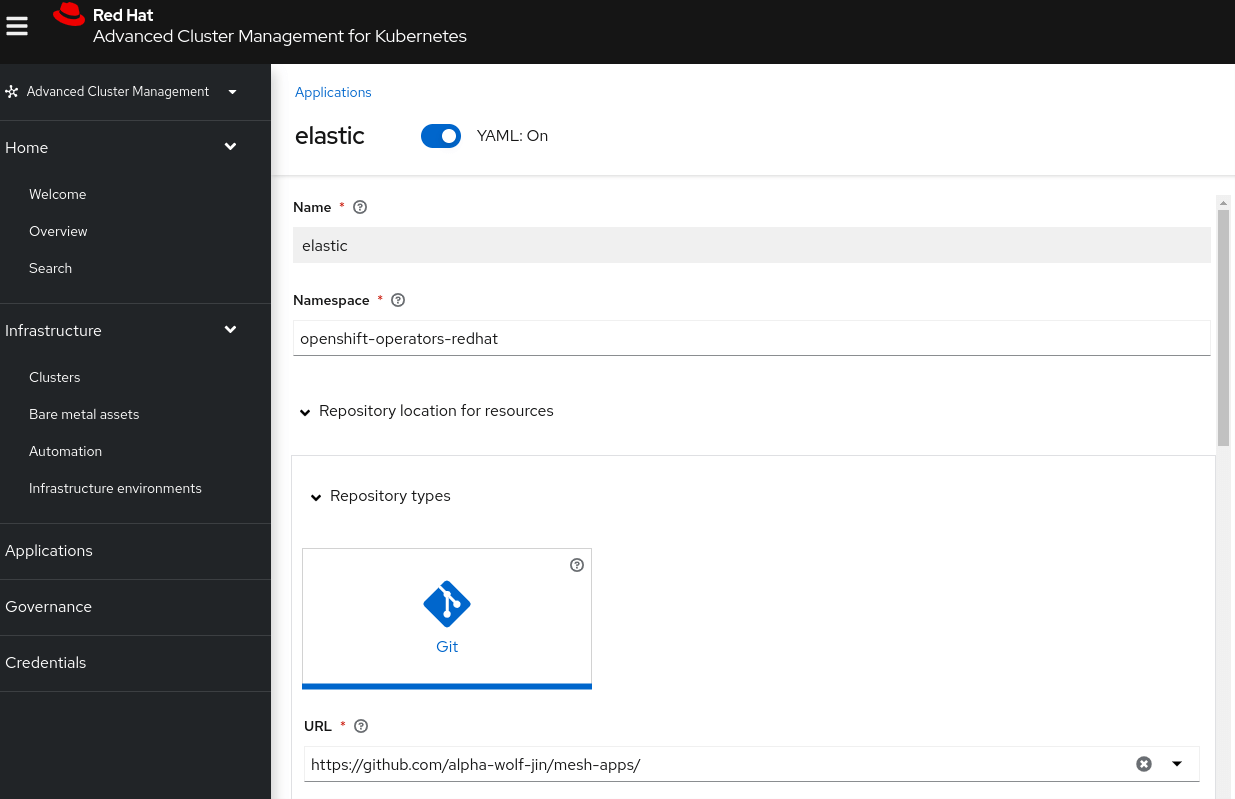
Use RHACM GitOps to create a new elastic application based on the following criteria
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| `Name` | elastic |
| `Namespace` | openshift-operators-redhat |
| `Repository types` | `Git` |
| `URL` | https://github.com/alpha-wolf-jin/mesh-apps/ |
| Branch | main |
| Path | elastic-operator |
| Label | purpose |
| Value | development |
| Deployment window | Always Active |
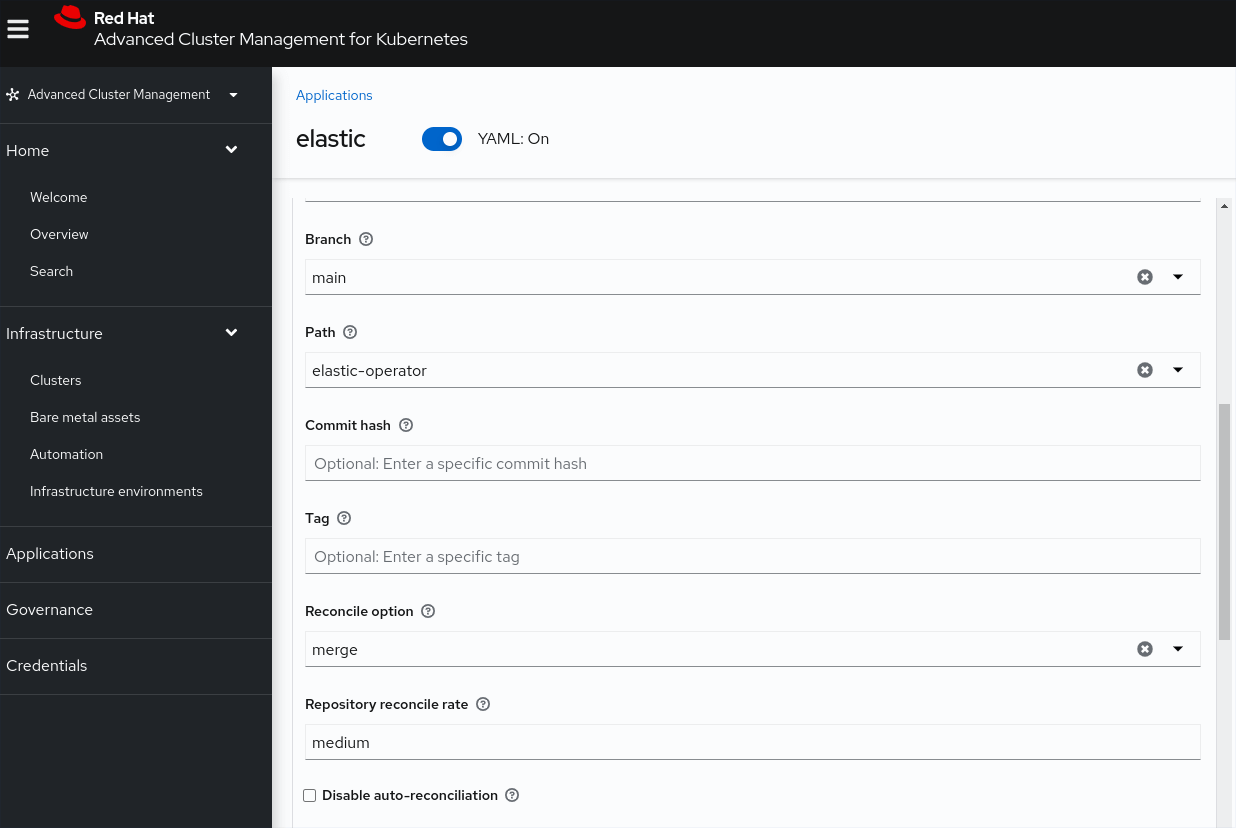
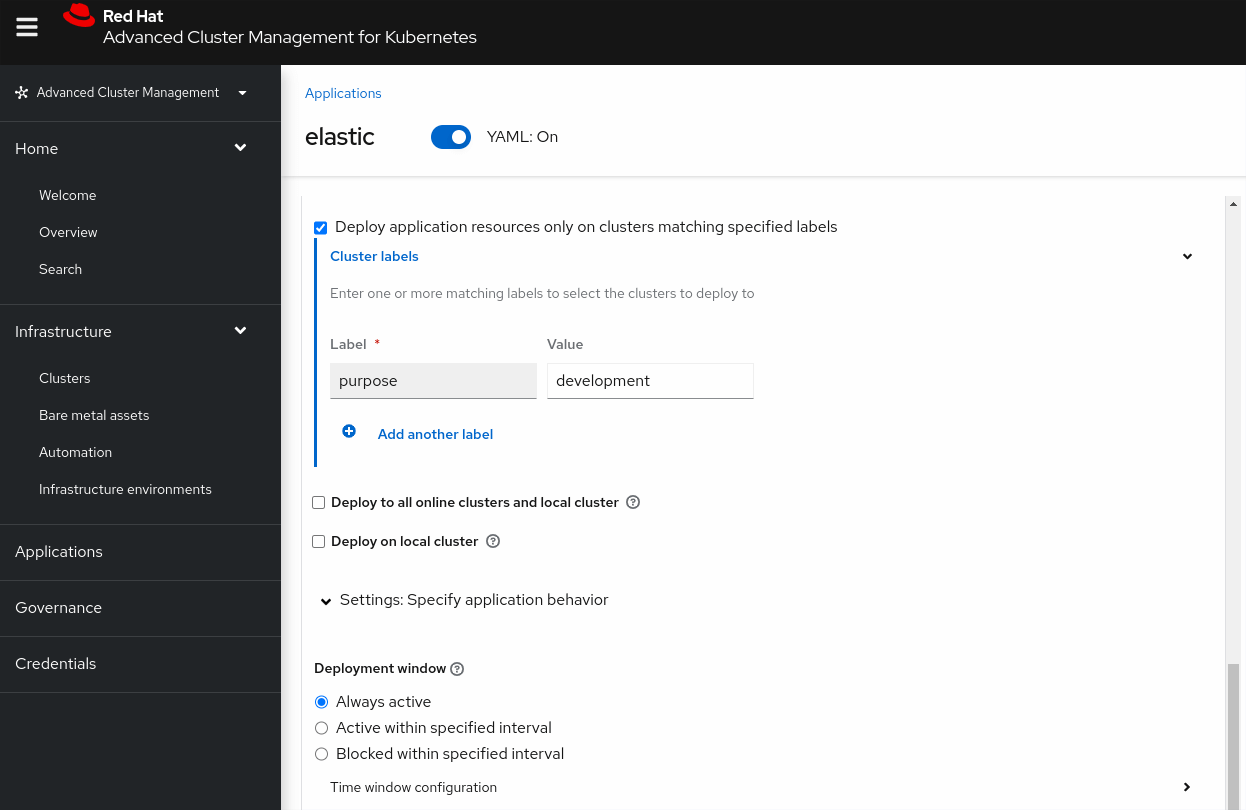
Click “ Create “
Application – jaeger-product
Use RHACM GitOps to create a new jaeger-product application based on the following criteria
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| `Name` | jaeger-product |
| `Namespace` | openshift-distributed-tracing |
| `Repository types` | `Git` |
| `URL` | https://github.com/alpha-wolf-jin/mesh-apps/ |
| Branch | main |
| Path | jaeger-operator |
| Label | purpose |
| Value | development |
| Deployment window | Always active |
Use RHACM GitOps to create a new kiali-servicemesh application based on the following criteria
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| `Name` | kiali-servicemesh |
| `Namespace` | openshift-operators |
| `Repository types` | `Git` |
| `URL` | https://github.com/alpha-wolf-jin/mesh-apps/ |
| Branch | main |
| Path | kiali-servicemesh-operator |
| Label | purpose |
| Value | development |
| Deployment window | Always active |
Use RHACM GitOps to create a new mesh application based on the following criteria
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| `Name` | mesh |
| `Namespace` | istio-system |
| `Repository types` | `Git` |
| `URL` | https://github.com/alpha-wolf-jin/mesh-apps/ |
| Branch | main |
| Path | mesh |
| Label | purpose |
| Value | development |
| Deployment window | Always Active |
Verify Service Mesh inside RHACM
Application – elastic
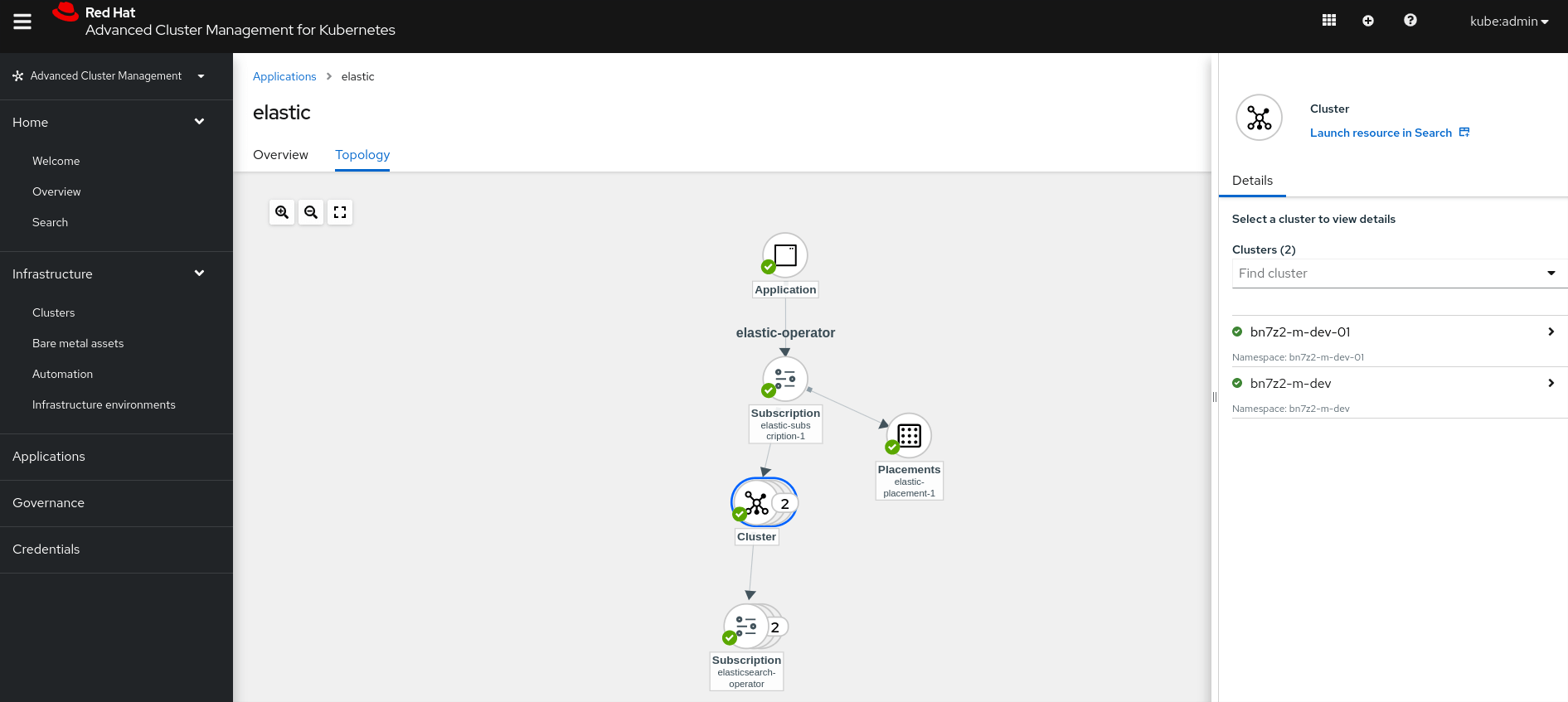
Application – jaeger-product
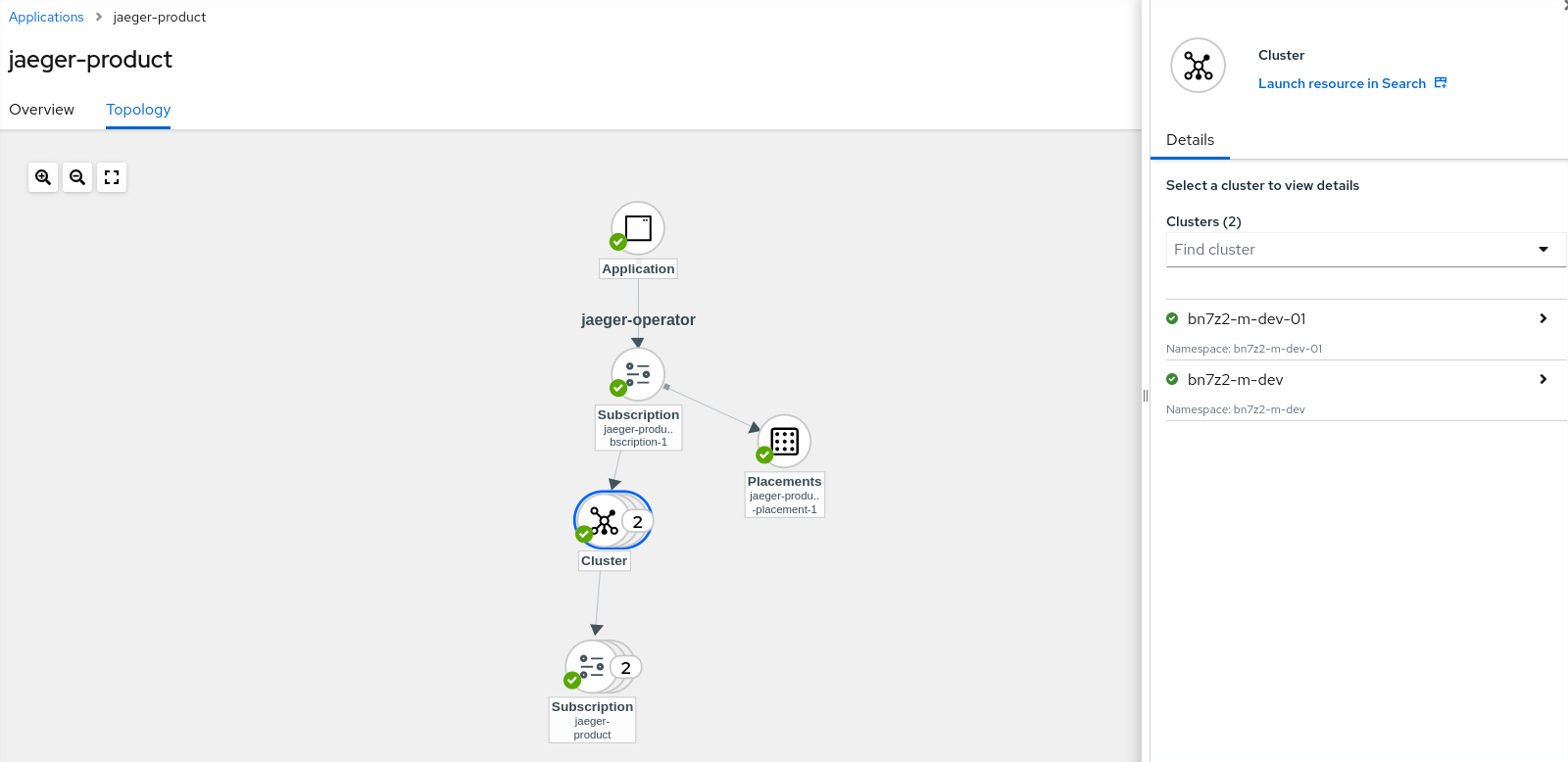
Application – kiali-servicemesh
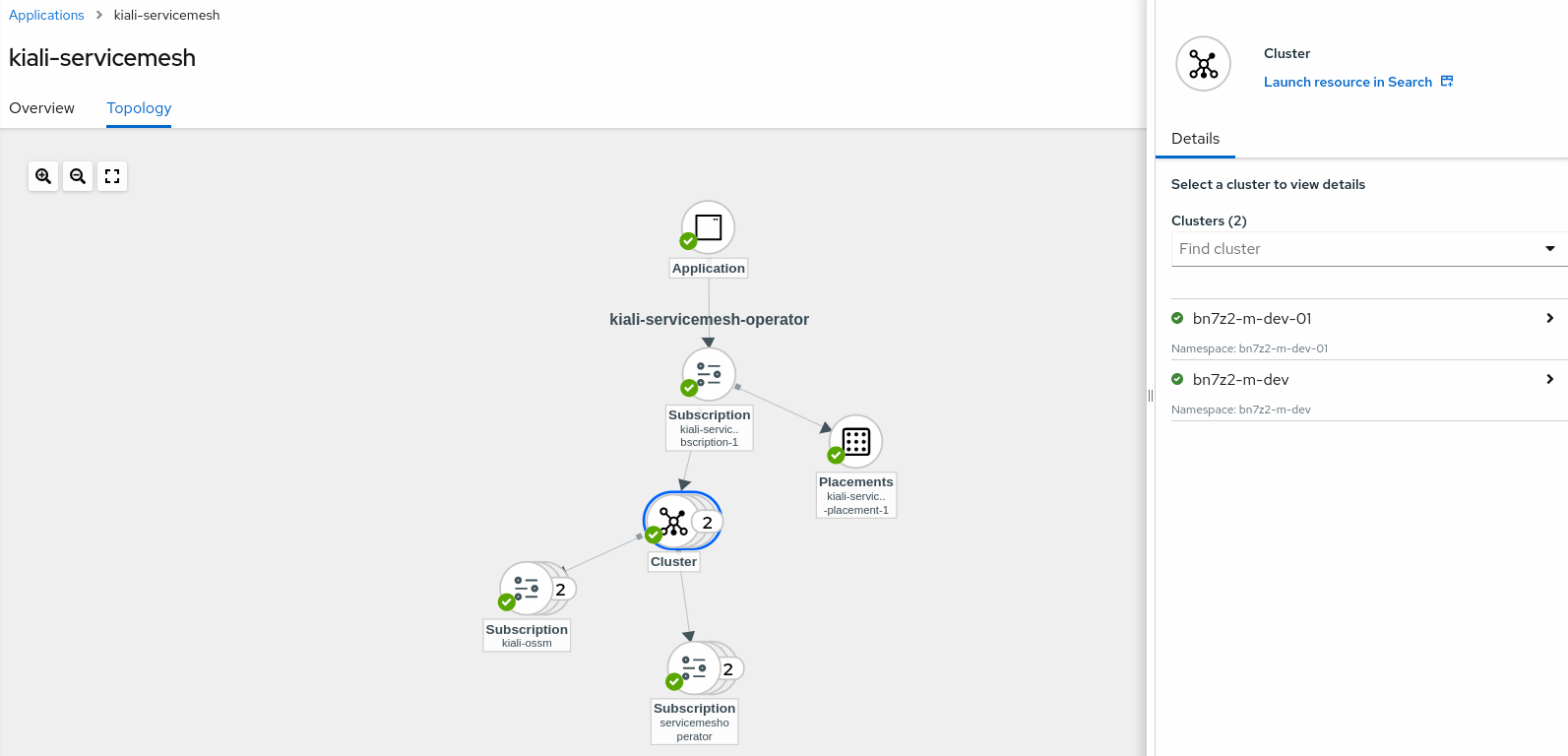
Application – mesh
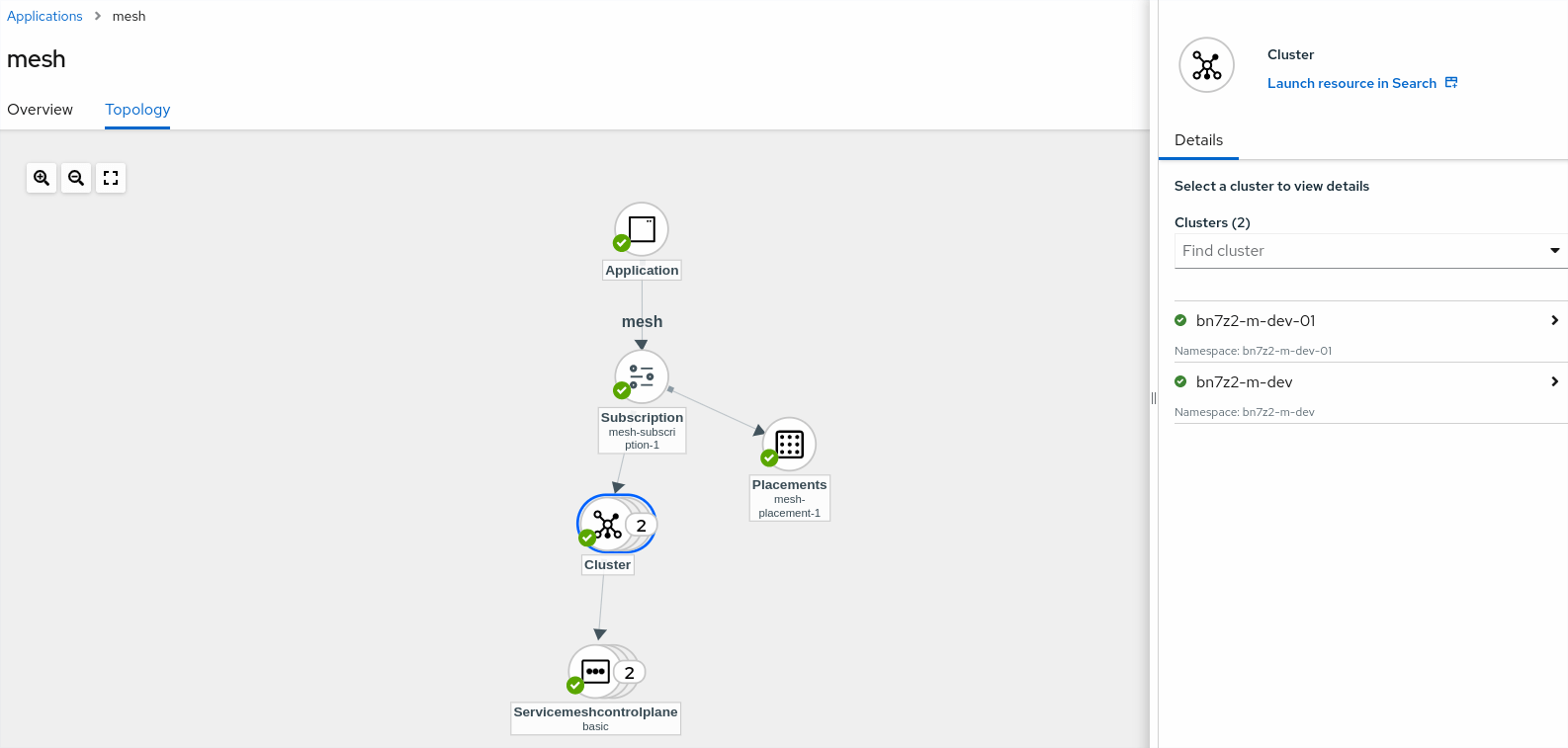
Verify Service Mesh inside Managed Clusters
Cluster 01
The smcp is ready.
$ oc login -u kubeadmin -p <password> https://api.bn7z2-m-dev-01.sandbox1558.opentlc.com:6443
Login successful.
$ oc get smcp -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS PROFILES VERSION AGE
basic 10/10 ComponentsReady ["default"] 2.2.3 18h
Cluster 02
The smcp is ready.
$ oc login -u kubeadmin -p <password> https://api.bn7z2-m-dev.sandbox1558.opentlc.com:6443
Login successful.
$ oc get smcp -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS PROFILES VERSION AGE
basic 0/0 DependencyMissingError 3h39m
The above is a small sample of how to manage the cluster with the RHACM GitOps.

Jin Zhang
I’m Jin, Red Hat ASEAN Senior Platform Consultant. My primary focus is Ansible Automation (Infrastructure as Code), OpenShift, and OpenStack.
Note
Disclaimer: The views expressed and the content shared in all published articles on this website are solely those of the respective authors, and they do not necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer or the techbeatly platform. We strive to ensure the accuracy and validity of the content published on our website. However, we cannot guarantee the absolute correctness or completeness of the information provided. It is the responsibility of the readers and users of this website to verify the accuracy and appropriateness of any information or opinions expressed within the articles. If you come across any content that you believe to be incorrect or invalid, please contact us immediately so that we can address the issue promptly.