Configure Your Windows Host to be Managed by Ansible
-
 Gineesh Madapparambath
Gineesh Madapparambath
- Ansible, Automation, Cloud
- December 1, 2020

I was talking to my friend about Ansible automation and how we are implementing automated solutions for cloud and on-premise infrastructure. Then he told me that, his team is looking for such tools to automate their Windows servers and Desktops. When I suggested Ansible, he didn’t believe me as he thought Ansible could not do anything with Windows machines! Oh.. then I realized that there are some misunderstandings about Ansible and its supported platforms as most of them thought Ansible is only available for Linux (or Unix); yes that is true (Ansible is not natively available for Windows yet) but you know, you can use Ansible to manage your Windows machines as well (and network devices, firewall devices, cloud , containers and more)
See other articles to learn how to manage Windows using Ansible
- Configure Your Windows Host to be Managed by Ansible
- How to open WinRM ports in the Windows firewall
- Ansible Windows Management using HTTPS and SSL
( Cover: Photo by Charles Parker from Pexels )
Also Read: Automation with Ansible Guides
Watch the video for a demo
Do you know, you have more than 100 Windows modules already available to use from the Ansible Community?
Read: Installing Ansible
But like Linux managed nodes, you need to configure some setups on your Windows machine as well, so that Ansible can talk to your Windows machine and execute automated tasks. And this guide is for you if you are struggling to configure your Windows machine to manage by Ansible .
Supported Windows Operating Systems
- Windows 7
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
Ansible Control Node Prerequisites
There is no special requirement on Ansible Engine or Ansible Controlnode, except winrm library. You need to install Python Winrm library for your Python environment.
$ pip install "pywinrm>=0.2.2"
## or
$ python3 -m pip install --user --ignore-installed pywinrm
Make sure, you have installed the winrm library on the exact Python environment Ansible is using. (Check ansible --version and see which Python version is used)
Windows Host Prerequisites for Ansible
Your Windows machine should meet the below requirements.
- PowerShell 3.0 or newer
- .NET 4.0 to be installed
- A WinRM listener should be created and activated
Check PowerShell Version
Open a PowerShell console and verify PowerShell version.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> (Get-Host).Version
Major Minor Build Revision
----- ----- ----- --------
5 1 14393 693
Configure WinRM
You need to configure listener and the service on the Windows machine as part of the WinRM setup. You have to execute a few steps in PowerShell for this, but fortunately, there is a readymade PowerShell script available in the Ansible repository called – ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1 . You can just download and execute the same on the Windows machine as below.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> $url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible-documentation/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
PS C:\Users\Administrator> $file = "$env:temp\ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
PS C:\Users\Administrator> (New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file)
PS C:\Users\Administrator> powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File $file
Self-signed SSL certificate generated; thumbprint: DD2BFCC45E7503BC9C05BA9174326B593614C733
wxf : http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/transfer
a : http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/08/addressing
w : http://schemas.dmtf.org/wbem/wsman/1/wsman.xsd
lang : en-US
Address : http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/08/addressing/role/anonymous
ReferenceParameters : ReferenceParameters
Ok.
PS C:\Users\Administrator>
If you are facing any SSL/TLS issues while downloading files, please check the TLS version you have configured. You can also use TLS1.2 explicitly as below.
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Note: If you have concerns about executing this readymade script (like the authentication it is using, the access policies etc), you can manually configure WinRM listener and the service by following WinRM setup documentation.
Ensure WinRM Ports are Open
Also make sure, ports 5985 and 5986 are open in the firewall (both OS as well as network side).
Read How to open WinRM ports in the Windows firewall.
That’s it, now you can access your Windows machine over WinRM and Ansible will be able to execute the playbook and tasks on your Windows machine.
Let us test Ansible to Windows Access
As you know, the first thing is you need to add your new machine to the inventory; something like below. I have added my new Windows machine under the host group called windows2016 .
[windows2016]
vm-win2016-dev ansible_host=10.1.10.101
Also need to configure other parameters like ansible_connection , ansible_port , user credentials etc. Either you can put it in the same inventory or under host_vars or group_vars . For this demo, I have put everything under group_vars/windows2016 .
$ cat group_vars/windows2016.yml
---
ansible_user: "Administrator"
ansible_password: "MyWindowsPassword2020"
ansible_port: "5986"
ansible_connection: "winrm"
ansible_winrm_transport: "basic"
ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation: ignore
Note: For production, you need to use a password encrypted using Ansible Vault or keep credentials in Ansible Tower. Also, you may need to create a different user rather than an Administrator .
Let’s run a very basic Ansible ad-hoc command with win_ping module.
$ ansible vm-win2016-dev -m win_ping
vm-win2016-dev | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Yes, Ansible can reach our Windows machine and is able to communicate. (Please note, the ping is not simple network ping, but Ansible will login to the machine and verify the access)
Fine, what about writing a playbook to create a new user on a Windows machine? Here see the very basic playbook and let’s test it.
---
- name: "Create New user on Windows Machine"
hosts: "{{ NODES }}"
tasks:
- name: "Check Windows machines access using win_ping"
win_ping:
when: ansible_os_family == 'Windows'
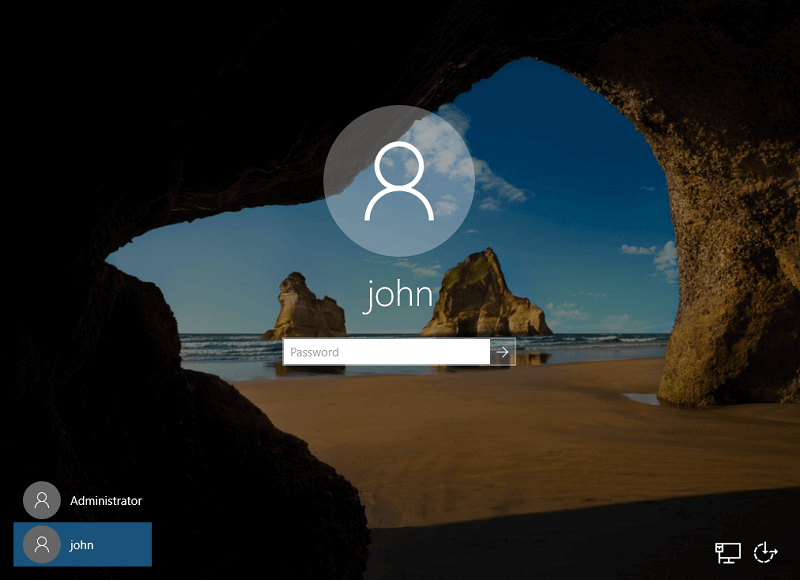
- name: Create a new User
win_user:
name: john
password: MyP4ssw0rd
state: present
groups:
- Users
when: ansible_os_family == 'Windows'
Execute the playbook using ansible-playbook command. Please note the NODES variable as I don’t usually hardcode the hosts inside the playbook; instead I pass the hosts list while running ansible-playbook command as shown below.
$ ansible-playbook test-access.yaml -e "NODES=windows"
PLAY [Testing Basic Connection to Managed Nodes] ***********************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************
ok: [10.6.1.216]
ok: [vm-win2016-dev]
TASK [Test Windows machines using win_ping] ****************************************************************
ok: [10.6.1.216]
ok: [vm-win2016-dev]
TASK [Create a new User] ***********************************************************************************
changed: [vm-win2016-dev]
changed: [10.6.1.216]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************
10.6.1.216 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
vm-win2016-dev : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Yes, it’s working and Ansible already completed all tasks successfully. Let’s go and check the Windows machine for new users.
Troubleshooting
If you are facing an error with the basic authentication, then check if the AllowUnencrypted option is enabled or not. You can enable the AllowUnencrypted option by using the following command. (Not recommended for a production environment)
PS C:\Users\Administrator>
winrm set winrm/config/service '@{AllowUnencrypted="true"}'
Service
RootSDDL = O:NSG:BAD:P(A;;GA;;;BA)(A;;GR;;;IU)S:P(AU;FA;GA;;;WD)(AU;SA;GXGW;;;WD)
MaxConcurrentOperations = 4294967295
MaxConcurrentOperationsPerUser = 1500
EnumerationTimeoutms = 240000
MaxConnections = 300
MaxPacketRetrievalTimeSeconds = 120
AllowUnencrypted = true
Auth
Basic = true
Kerberos = true
Negotiate = true
Certificate = false
CredSSP = false
CbtHardeningLevel = Relaxed
DefaultPorts
HTTP = 5985
HTTPS = 5986
IPv4Filter = *
IPv6Filter = *
EnableCompatibilityHttpListener = false
EnableCompatibilityHttpsListener = false
CertificateThumbprint
AllowRemoteAccess = true

Gineesh Madapparambath
Gineesh Madapparambath is the founder of techbeatly. He is the co-author of The Kubernetes Bible, Second Edition and the author of Ansible for Real Life Automation. He has worked as a Systems Engineer, Automation Specialist, and content author. His primary focus is on Ansible Automation, Containerisation (OpenShift & Kubernetes), and Infrastructure as Code (Terraform). (Read more: iamgini.com)
Note
Disclaimer: The views expressed and the content shared in all published articles on this website are solely those of the respective authors, and they do not necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer or the techbeatly platform. We strive to ensure the accuracy and validity of the content published on our website. However, we cannot guarantee the absolute correctness or completeness of the information provided. It is the responsibility of the readers and users of this website to verify the accuracy and appropriateness of any information or opinions expressed within the articles. If you come across any content that you believe to be incorrect or invalid, please contact us immediately so that we can address the issue promptly.
Tags :
- Ansible
- Automation
- Cloud
- Infrastructre & hardware
- Ansible and windows
- Ansible automation
- Ansible windows automation
- Ansible windows configuration
- Ansible windows guide
- Ansible windows setup
- Automate windows using ansible
- Configure windows to access by ansible
- How to manage windows from ansible
- Manage windows using ansible
- Windows and ansible